Implement IaaS solutions
Provision virtual machines in Azure
Design considerations for virtual machine creation
- Availability
- VM size
- VM limits
- VM image
- VM disks
Why choose Azure Resource Manager templates?
If you’re trying to decide between using Azure Resource Manager templates and one of the other infrastructure as code services, consider the following advantages of using templates:
-
Declarative syntax: Azure Resource Manager templates allow you to create and deploy an entire Azure infrastructure declaratively. For example, you can deploy not only virtual machines, but also the network infrastructure, storage systems, and any other resources you may need.
-
Repeatable results: Repeatedly deploy your infrastructure throughout the development lifecycle and have confidence your resources are deployed in a consistent manner. Templates are idempotent, which means you can deploy the same template many times and get the same resource types in the same state. You can develop one template that represents the desired state, rather than developing lots of separate templates to represent updates.
-
Orchestration: You don’t have to worry about the complexities of ordering operations. Resource Manager orchestrates the deployment of interdependent resources so they’re created in the correct order. When possible, Resource Manager deploys resources in parallel so your deployments finish faster than serial deployments. You deploy the template through one command, rather than through multiple imperative commands.
deployment mode
- Complete mode
- Incremental mode
Exercise: Create and deploy Azure Resource Manager templates by using Visual Studio Code
1
2
3
4
| # Create resource group
az group create --name az204-arm-rg --location westeurope
# Deploy storage account using arm
az deployment group create --resource-group az204-arm-rg --template-file azuredeploy.json --parameters azuredeploy.parameters.json
|
Manage container images in Azure Container Registry
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| # Download Dockerfile example
echo FROM mcr.microsoft.com/hello-world > Dockerfile
az acr build -h
# Build image and push it to acr
az acr build -t sample/hello-world -r sfanacr .
# List the repos in your acr
az acr repository list -n sfanacr
# Run container image remotely
az acr run -r sfanacr --cmd '$Registry/sample/hello-world' /dev/null
# Run container locally
## login to acr
az acr login -n sfanacr
Login Succeeded
docker run sfanacr.azurecr.io/sample/hello-world
|
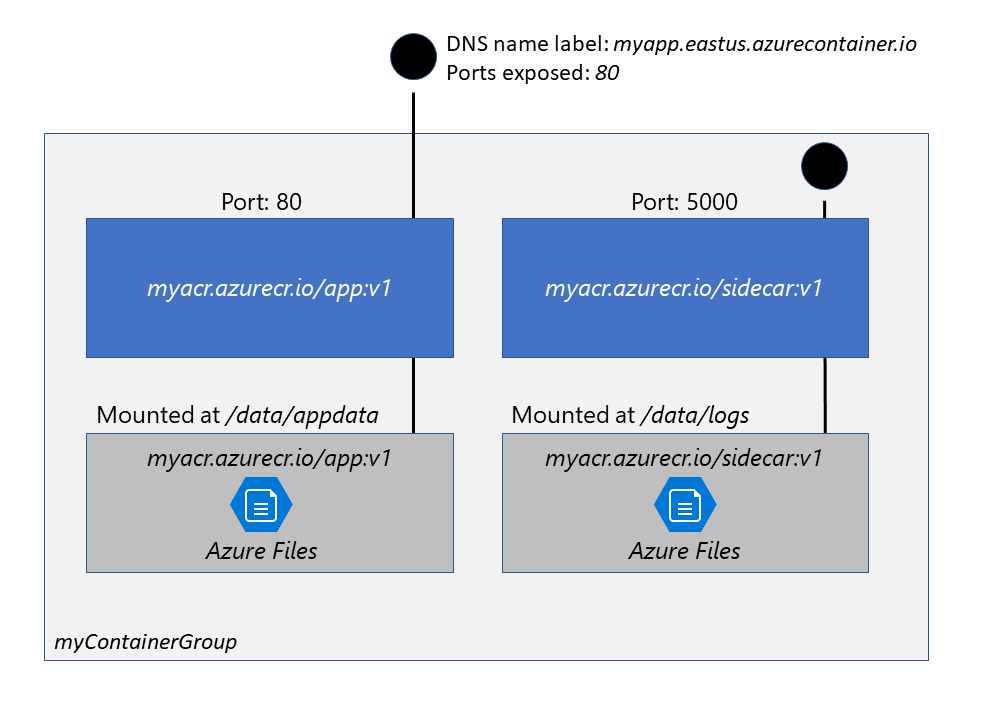
Run container images in Azure Container Instances
- Fast startup: ACI can start containers in Azure in seconds, without the need to provision and manage VMs
- Container access: ACI enables exposing your container groups directly to the internet with an IP address and a fully qualified domain name (FQDN)
- Hypervisor-level security: Isolate your application as completely as it would be in a VM
- Customer data: The ACI service stores the minimum customer data required to ensure your container groups are running as expected
- Custom sizes: ACI provides optimum utilization by allowing exact specifications of CPU cores and memory
- Persistent storage: Mount Azure Files shares directly to a container to retrieve and persist state
- Linux and Windows: Schedule both Windows and Linux containers using the same API.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| DNS_NAME_LABEL=aci-fan-$RANDOM
# create a container
az container create --resource-group az204-arm-rg \
--name mycontainer \
--image mcr.microsoft.com/azuredocs/aci-helloworld \
--ports 80 \
--dns-name-label $DNS_NAME_LABEL --location westeurope
# Set restart policy
--restart-policy OnFailure
# Set environment variables
--environment-variables 'NumWords'='5' 'MinLength'='8'
# Mount volume
--azure-file-volume-account-name $ACI_PERS_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME \
--azure-file-volume-account-key $STORAGE_KEY \
--azure-file-volume-share-name $ACI_PERS_SHARE_NAME \
--azure-file-volume-mount-path /aci/logs/
# Verify the container is running
az container show --resource-group az204-arm-rg \
--name mycontainer
# clean up resource
az container delete -g az204-arm-rg -n $DNS_NAME_LABEL
|
Create Azure App Service Web Apps
create an Azure App Service Web App
The pricing tier of an App Service plan determines what App Service features you get and how much you pay for the plan. There are a few categories of pricing tiers:
- Shared compute: Both Free and Shared share the resource pools of your apps with the apps of other customers. These tiers allocate CPU quotas to each app that runs on the shared resources, and the resources can’t scale out.
- Dedicated compute: The Basic, Standard, Premium, PremiumV2, and PremiumV3 tiers run apps on dedicated Azure VMs. Only apps in the same App Service plan share the same compute resources. The higher the tier, the more VM instances are available to you for scale-out.
- Isolated: This tier runs dedicated Azure VMs on dedicated Azure Virtual Networks. It provides network isolation on top of compute isolation to your apps. It provides the maximum scale-out capabilities.
- Consumption: This tier is only available to function apps. It scales the functions dynamically depending on workload
enable diagnostics logging
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/troubleshoot-diagnostic-logs
deploy code to a web app
Automated deployment
Manual deployment
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| # create dotnet core webapi
dotnet new webapi
# verify locally
dotnet build
dotnet run
# deploy the webapi to Azure web app using vscode
curl https://sfan.azurewebsites.net/WeatherForecast
|
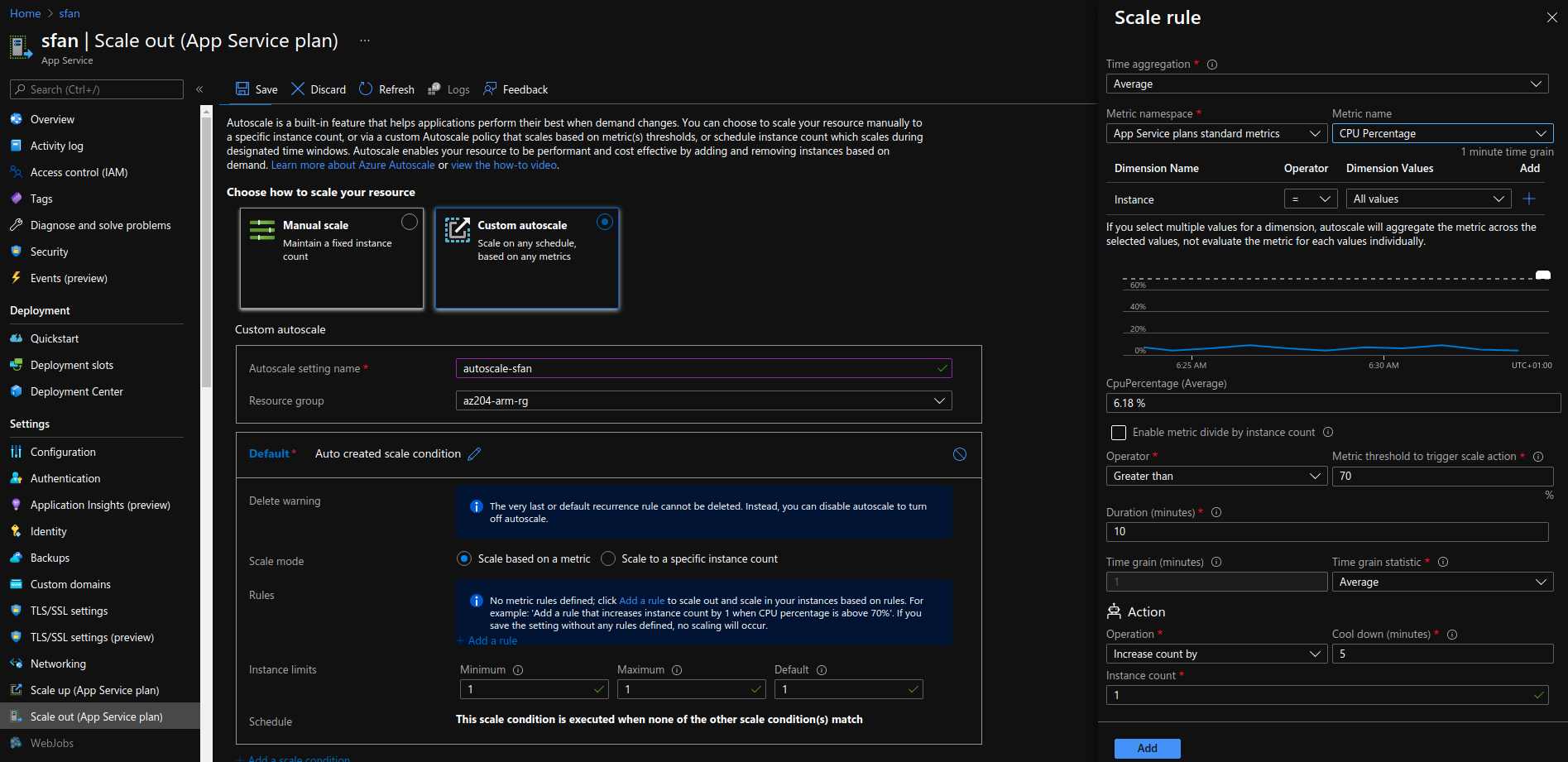
implement autoscaling rules
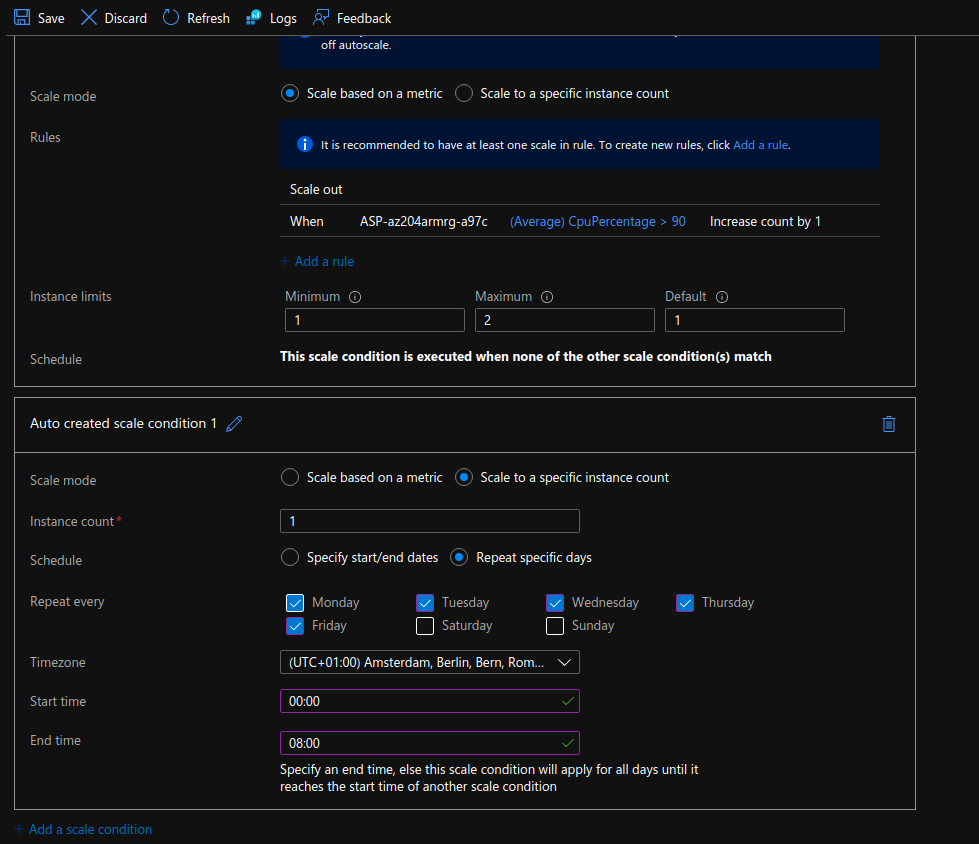
- autoscaling by operational or system metrics
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-monitor/autoscale/autoscale-get-started
Implement Azure functions
create and deploy Azure Functions apps
1
2
| az functionapp create -g az204-arm-rg -p ASP-az204armrg-a97c -n az204-sfan-fa -s az204storageacctarm --runtime dotnet
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| {
"bindings": [
{
"name": "myQueueItem",
"type": "rabbitMQTrigger",
"direction": "in",
"queueName": "",
"connectionStringSetting": ""
}
]
}
|
implement function triggers by using data operations, timers, and webhooks
RabbitMQ trigger:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/functions-bindings-rabbitmq-trigger?tabs=csharp#example
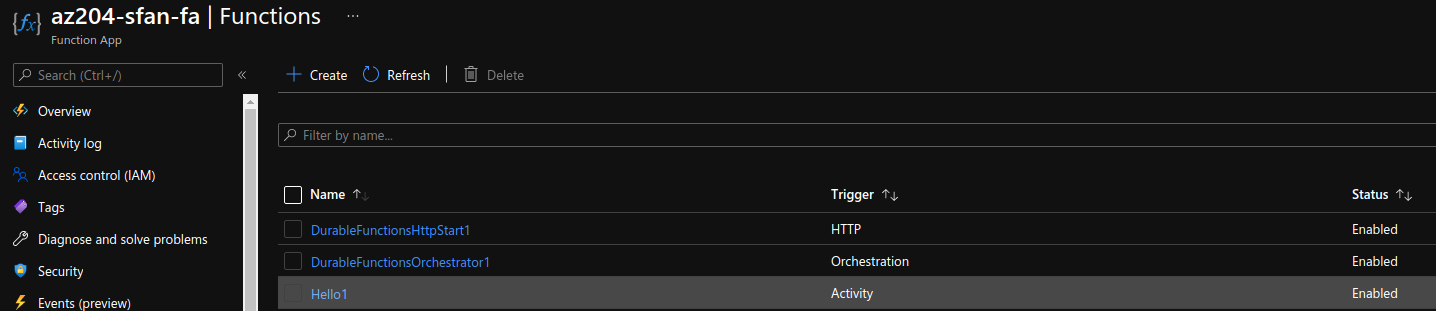
implement Azure Durable Functions
Durable Functions enables you to implement complex stateful functions in a serverless-environment.
Function types
- Client functions
- Orchestrator functions describe how actions are executed, and the order in which they are run. You write the orchestration logic in code (C# or JavaScript).
- Activity functions
1
2
3
4
| az functionapp show -g az204-arm-rg -n az204-sfan-fa
az functionapp function show -g az204-arm-rg -n az204-sfan-fa --function-name DurableFunctionsHttpStart1
az functionapp function show -g az204-arm-rg -n az204-sfan-fa --function-name DurableFunctionsOrchestrator1
az functionapp function show -g az204-arm-rg -n az204-sfan-fa --function-name Hello1
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| {
"name":"DurableFunctionsOrchestrator1",
"instanceId":"d493194255e44c1cbb7bcb67a5db65b0",
"runtimeStatus":"Completed",
"input":{
"body":"sfan"
},
"customStatus":null,
"output":[
"Hello Tokyo!",
"Hello Seattle!",
"Hello London!"
],
"createdTime":"2021-11-07T07:27:31Z",
"lastUpdatedTime":"2021-11-07T07:27:32Z"
}
|
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/create-long-running-serverless-workflow-with-durable-functions/2-what-is-durable-functions
implement custom handlers
Azure Functions features a variety of language runtimes. If your language of choice is not provided by default, you can use a custom handler.
For your app to work with HTTP primitives, you need to configure a few things:
- Listen to a custom handler port
- Configure the default executable path
- Enable request forwarding
1
2
3
| "customHandler": {
"defaultExecutablePath": "mygoapp.exe"
}
|
Develop solutions that use Cosmos DB storage
Solutions that benefit from Azure Cosmos DB
Any web, mobile, gaming, and IoT application that needs to handle massive amounts of data, reads, and writes at a global scale with near-real response times for a variety of data will benefit from Cosmos DB’s guaranteed high availability, high throughput, low latency, and tunable consistency.
Choose an API in Azure Cosmos DB
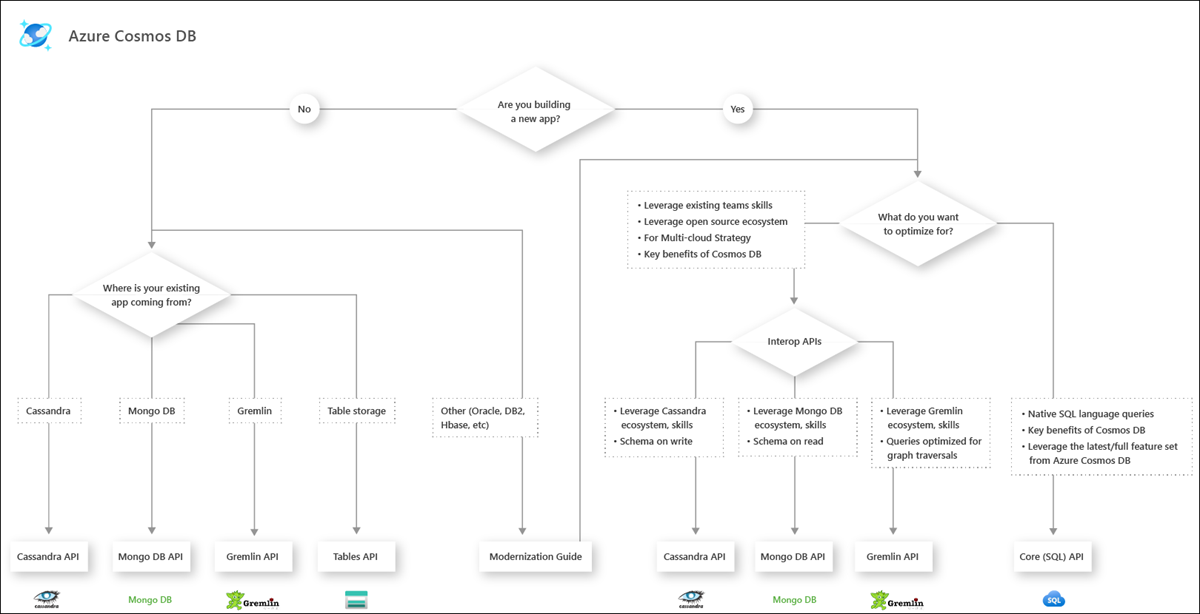
Data modeling in Azure Cosmos DB
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/sql/modeling-data
Partition data
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/partitioning-overview
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/sql/how-to-model-partition-example
set the appropriate consistency level for operations
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/consistency-levels
1
2
3
4
5
6
| "consistencyPolicy": {
"defaultConsistencyLevel": "Session",
"maxIntervalInSeconds": 5,
"maxStalenessPrefix": 100
},
|
Blob storage
Move items in Blob storage between storage accounts or containers
1
2
3
4
5
6
| # Azure CLI
az storage copy -s https://az204storageacctarm.blob.core.windows.net/azure-webjobs-secrets -d https://az204storageacctarm.blob.core.windows.net/sfan --recursive --account-key xxx
# AzCopy
# .NET Storage Client library
|
Blob containers support system properties and user-defined metadata, in addition to the data they contain.
Retrieving properties and metadata via REST
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| curl -I https://lcdev.blob.core.windows.net/development/assets/00_featured_shrek_smiling_in_mud_bath_0688afc539.jpeg
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 49134
Content-Type: image/jpeg
Last-Modified: Fri, 23 Jul 2021 14:24:54 GMT
ETag: 0x8D94DE5A43E00EE
Vary: Origin
Server: Windows-Azure-Blob/1.0 Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
x-ms-request-id: 48957174-c01e-008a-4827-dbb11f000000
x-ms-version: 2009-09-19
x-ms-lease-status: unlocked
x-ms-blob-type: BlockBlob
Date: Tue, 16 Nov 2021 20:24:17 GMT
|
Azure Blob storage lifecycle
Blob storage is designed for:
- Serving images or documents directly to a browser.
- Storing files for distributed access.
- Streaming video and audio.
- Writing to log files.
- Storing data for backup and restore, disaster recovery, and archiving.
- Storing data for analysis by an on-premises or Azure-hosted service.
1
2
| # create block blob storage account
|
Azure storage offers different access tiers, allowing you to store blob object data in the most cost-effective manner. Available access tiers include:
- Hot - Optimized for storing data that is accessed frequently.
- Cool - Optimized for storing data that is infrequently accessed and stored for at least 30 days.
- Archive - Optimized for storing data that is rarely accessed and stored for at least 180 days with flexible latency requirements, on the order of hours.
Implement Azure security
Implement user authentication and authorization
Microsoft identity platform
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/implement-authentication-by-using-microsoft-authentication-library/4-interactive-authentication-msal
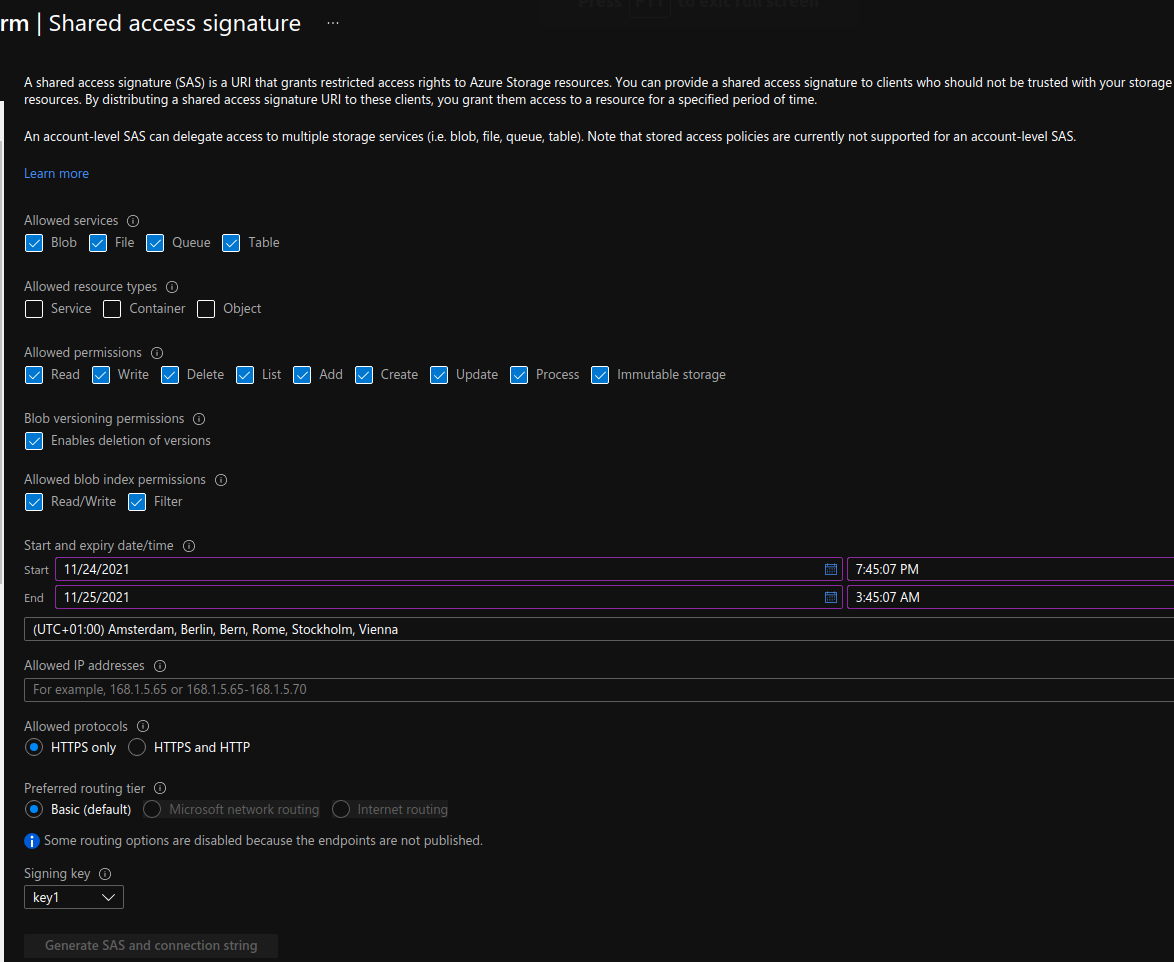
Implement shared access signatures
A shared access signature (SAS) is a URI that grants restricted access rights to Azure Storage resources. You can provide a shared access signature to clients that you want grant delegate access to certain storage account resources.
Implement secure cloud solutions
secure app configuration data by using App Configuration Azure Key Vault
Enable managed identity on azure app service
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| az webapp identity assign \
--resource-group learn-2cdbb38a-41ed-4c3b-8e2a-a9c94457cd1e \
--name keyvault-sfan-app
{
"principalId": "40d7d056-5836-4e46-a61d-1887ba4259c0",
"tenantId": "604c1504-c6a3-4080-81aa-b33091104187",
"type": "SystemAssigned",
"userAssignedIdentities": null
}
|
The last step before deploying is to assign Key Vault permissions to your app’s managed identity. Make sure to enter both your unique vault name to the –name parameter, and enter the principalId value you copied from the previous step as the value for object-id in the following command. To establish Get and List access, run this command.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| # assign permissions
az keyvault set-policy \
--secret-permissions get list \
--name learn-sfan \
--object-id 40d7d056-5836-4e46-a61d-1887ba4259c0
# deploy app
dotnet publish -o pub
zip -j site.zip pub/*
az webapp deployment source config-zip \
--src site.zip \
--resource-group learn-2cdbb38a-41ed-4c3b-8e2a-a9c94457cd1e \
--name keyvault-sfan-app
|
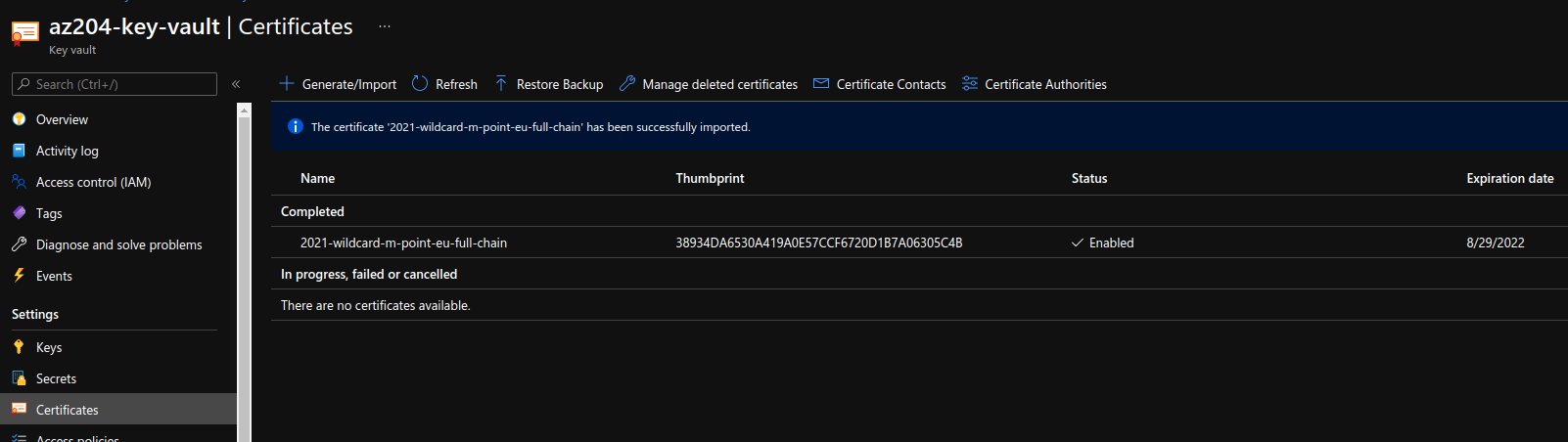
develop code that uses keys, secrets, and certificates stored in Azure Key Vault
import certificate into key vault
implement Managed Identities for Azure resources
Reference