- inbound
Outbound
Backend
- C
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-monitor/app/custom-operations-tracking
Y X N
Y
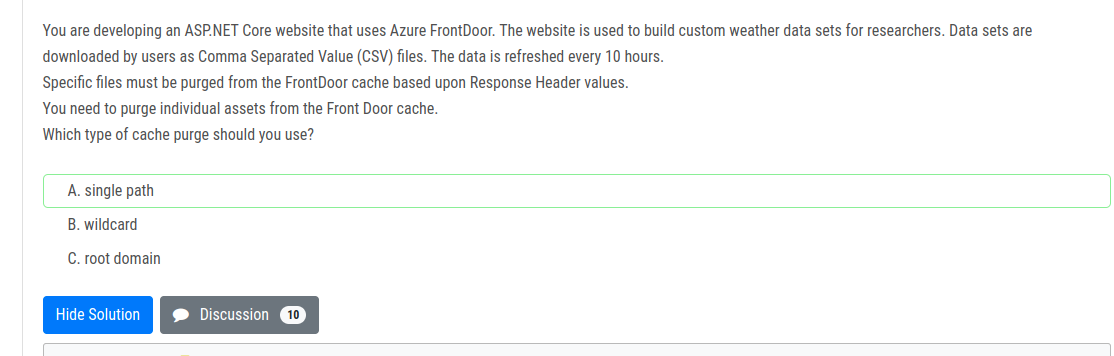
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/frontdoor/front-door-caching
1 hour
Cache every unique URL
Enable
Add
Configure
N
N
Instead deploy and configure Azure Cache for Redis. Update the web applications.
ICache X IDatabase ValueDel
Create trigger on message Action to read IoT Add a condition to compare Add to send email
Funnels
Impact
User flows X Retention
User flows
Retention - how many users come back?
Users tool: How many people used your app and its features. Users are counted by using anonymous IDs stored in browser cookies. A single person using different browsers or machines will be counted as more than one user.
Sessions tool: How many sessions of user activity have included certain pages and features of your app. A session is counted after half an hour of user inactivity, or after 24 hours of continuous use.
Events tool: How often certain pages and features of your app are used. A page view is counted when a browser loads a page from your app, provided you’ve instrumented it.
Funnel: If your application involves multiple stages, you need to know if most customers are progressing through the entire process, or if they’re ending the process at some point. The progression through a series of steps in a web application is known as a funnel
User flows:
B X A
AD
A
A
ago
distinct
where
summarize count()
–docker-container-log
webapp
tail
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
az webapp log config -h
Command
az webapp log config : Configure logging for a web app.
Arguments
--application-logging : Configure application logging. Allowed values: azureblobstorage,
filesystem, off.
--detailed-error-messages : Configure detailed error messages. Allowed values: false, true.
--docker-container-logging : Configure gathering STDOUT and STDERR output from container.
Allowed values: filesystem, off.
--failed-request-tracing : Configure failed request tracing. Allowed values: false, true.
--level : Logging level. Allowed values: error, information, verbose,
warning.
--slot -s : The name of the slot. Default to the productions slot if not
specified.
--web-server-logging : Configure Web server logging. Allowed values: filesystem, off.
az webapp log -h
Group
az webapp log : Manage web app logs.
Subgroups:
deployment [Preview] : Manage web app deployment logs.
Commands:
config : Configure logging for a web app.
download : Download a web app's log history as a zip file.
show : Get the details of a web app's logging configuration.
tail : Start live log tracing for a web app.
There are four types of availability tests:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-monitor/app/availability-overview
internal X External
consumption plan doesn’t support build-in cache.
private
Authorization
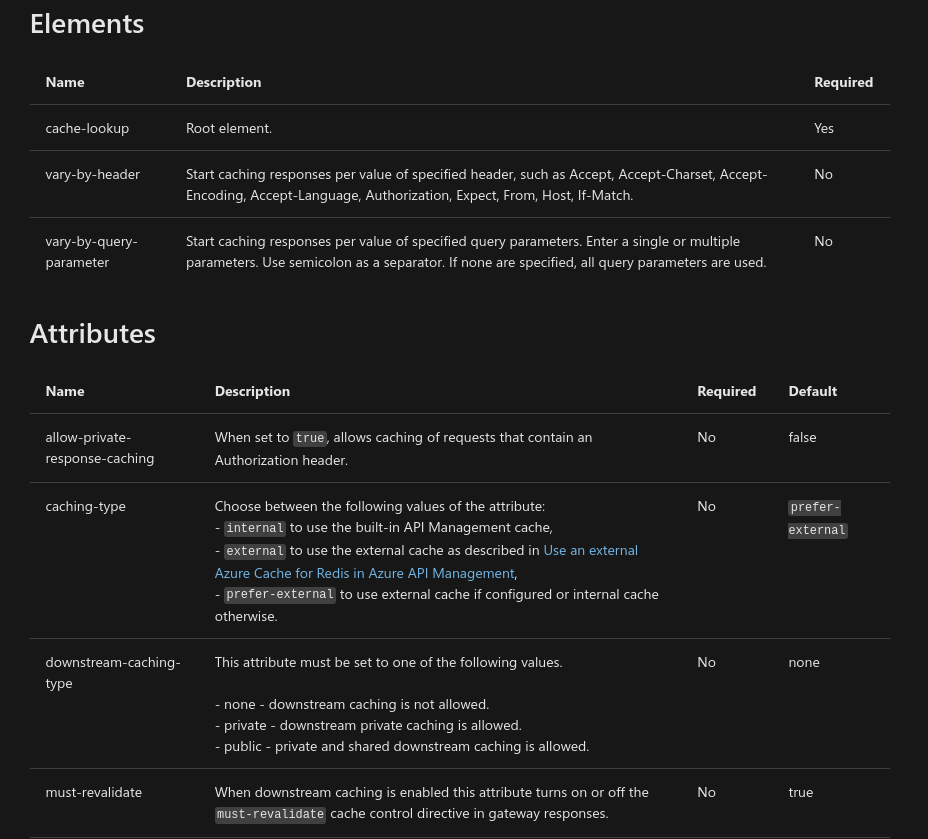
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/api-management/api-management-caching-policies#CachingPolicies
D
A
Register -> Build -> Create auth provider -> Create new instance -> Invoke
Storage -> Log Analytics -> diagnostic settings to Azure Logic App
X
Log Analytics -> Install LogicApp Management solution -> diagnostic settings to Azure Logic App
To set up logging for your logic app, you can enable Log Analytics when you create your logic app, or you can install the Logic Apps Management solution in your Log Analytics workspace for existing logic apps.
X
Log -> VMInsight -> Install -> ApplicationInsight
In app registration, select New registration
Select Azure AD
Wrong
In app registration, select New registration
Select Azure AD
Create a new application
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/quickstart-register-app
Prerequisites:
A working Azure AD tenant with at least an Azure AD Premium P1 or trial license enabled.
The recommended way to enable and use Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication is with Conditional Access policies.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/authentication/tutorial-enable-azure-mfa
C
B
Y
Y
Purge protection
9. client_id, application, profile X
UseAuth UseAuthorization UseAzureAppConfiguration
C
Y
Y X
The requirement is to save scanned copies of patient intake forms. Which is kind of unstructured data, should not be saved with cosmos db. Using azure blob storage instead.
N
keyvault
keyvault key
vm
vm encryption
data X all
X
5->3->2->1->4
N
Y X
Role-based access control is used for authorization and not authentication.
iPhone X iOS
Header
User_agent
iPhone
Y
optionalClaims
requiredResourceAccess
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-US/azure/active-directory/develop/reference-app-manifest?WT.mc_id=Portal-Microsoft_AAD_RegisteredApps
B
B X A
D
Inbound
Inbound
Outbound Outbound
ClientSecretCredential X DefaultAzureCredential
This example is using ‘DefaultAzureCredential()’ class from Azure Identity Library, which allows to use the same code across different environments with different options to provide identity. For more information about authenticating to key vault, see Developer’s Guide.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/key-vault/secrets/quick-create-net#authenticate-and-create-a-client
31. AC X AD
The question requires to use SAS token, C is not correct.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/rest/api/storageservices/create-user-delegation-sas#revoke-a-user-delegation-sas
X
Generate KEK-> Retrieve KEk-> Generate key blob-> key import
User steps To perform a key transfer, a user performs following steps:
Customers use the BYOK tool and documentation provided by HSM vendor to complete Steps 3. It produces a Key Transfer Blob (a “.byok” file).
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/key-vault/keys/byok-specification
A
YYYY
AC
36. Y X N
N
Y
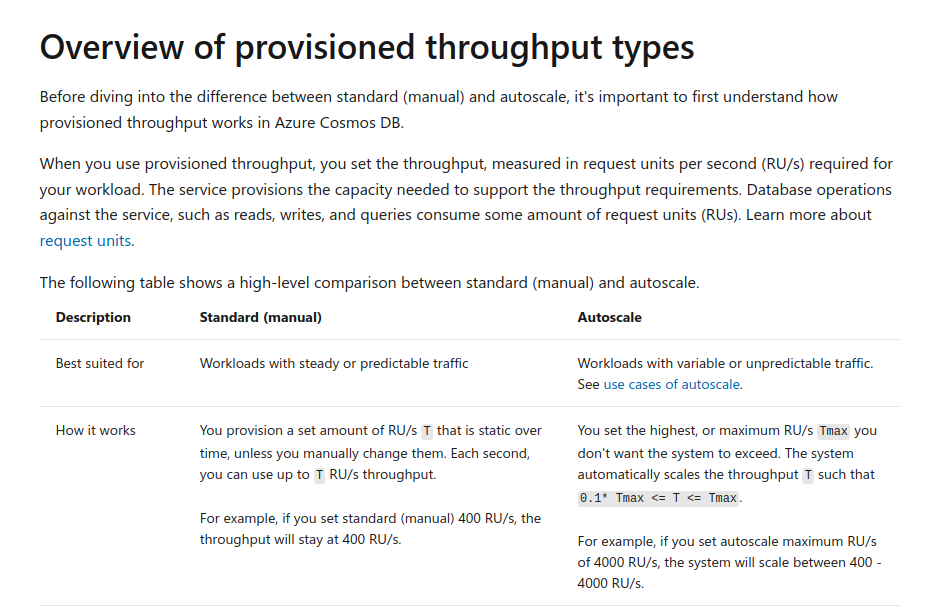
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/how-to-choose-offer
Builder scopes